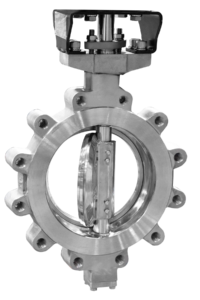
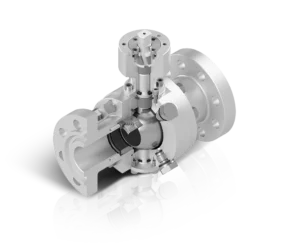
About
Along with polypropylene, polyethylene is one of the most common polymeric materials. It has a number of advantages, such as resistance to impact and frost, to acids, alkalis and salts, as well as absolute water resistance, and is therefore used in many industries: packaging, automotive, textiles and fibers, as well as in agriculture and the pharmaceutical industry
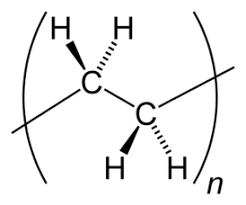
Process features
Polyethylene is produced by polymerization of ethylene at high temperatures (up to +300C) and low (up to 0.8 MPa) or high pressure (up to 300 MPa) in the presence of a catalyst. Low pressure ethylene polymerization can be carried out by 3 different methods: polymerization in solution, in suspension and in the gas phase. Depending on the technology there are 3 main grades of polyethylene: low density polyethylene, linear low density polyethylene, high density polyethylene.